Melero, Francisco Javier Tecnologías digitales aplicadas al patrimonio universitario Artículo de revista Revista PH Instituto Andaluz del Patrimonio Histórico, 113 (1), pp. 170-185, 2024, ISSN: 2340-7565. Melero, Francisco Javier ; Bellido-Gant, Maria Luisa University heritage and technologies : Current Experiences in Andalucia Artículo de revista MUSEA. Journal for museology, museum practice and audience, 1 (1), pp. 160-169, 2024. Hernández-Bautista, Marina ; Melero, Francisco Javier Deep learning of curvature features for shape completion Artículo de revista Computers & Graphics, 115 , pp. 204-215, 2023. Alonso, Sergio; Montes, Rosana; Molina, Daniel; Palomares, Ivan; Martínez-Cámara, Eugenio; Chiachío, Manuel; Chiachío, Juan; Melero, Francisco Javier ; García Moral, Pablo ; Fernández, Bárbara; Moral, Cristina; Marchena, Rosario; Pérez de Vargas, Javier ; Herrera, Francisco Ordering Artificial Intelligence Based Recommendations to Tackle the SDGs with a Decision-Making Model Based on Surveys Artículo de revista Sustainability, 13 (11), 2021, ISBN: 2071-1050. Montes, Rosana; Melero, Francisco Javier ; Palomares, Iván ; Alonso, Sergio; Chiachío, Juan; Chiachío, Manuel; Molina, Daniel; Martínez-Cámara, Eugenio ; Tabik, Siham; Herrera, Francisco Inteligencia Artificial y Tecnologías Digitales para los ODS Libro Real Academia de Ingeniería, 2021. Melero, Francisco Javier ; Fuentes, M M V Workshop Internacional de Investigación en Emprendimiento GEM-ACEDE, 2020, ISBN: 978-84-09-23683-1. Melero, F J Nuevas tecnologías para la documentación y difusión del patrionio cofrade Capítulo de libro Valverde, Crespo
J.M. F J (Ed.): La Semana Santa de Granada: Pasado, presente y futuro, pp. 151-191, Ed. Nuevo Inicio, Granada, 2020. Melero, Francisco Javier ; Garcia, Manuela; Bellido-Gant, Maria Luisa Atalaya3D: Disseminating Andalusian Public Universities’ Heritage through 3D and Web Technologies Artículo de revista University Museums and Collections Journal (UMACJ), 11 (1), pp. 43, 2019, ISSN: 2071-7229. Melero, F J; Aguilera, A; Feito, F Fast collision detection between high resolution polygonal models Artículo de revista Computers & Graphics, 83 , pp. 97-106, 2019, ISSN: 0097-8493. Melero, Francisco Javier; Revelles, Jorge; Bellido, Maria Luisa Atalaya3D: Making Universities' Cultural Heritage Accessible Through 3D Technologies Artículo en actas Sablatnig, Robert; Wimmer, Michael (Ed.): Eurographics Workshop on Graphics and Cultural Heritage, pp. 31-35, The Eurographics Association, 2018, ISSN: 2312-6124. Melero, F J; Pelechano, N CEIG 2017. Proceedings of the XXVII Spanish Computer Graphics Conference Acta de congreso Eurographics Sección Española, EGSE The Eurographics Association, Sevilla, 2017, ISBN: 978-3-03868-046-8. Bolívar, F J; Melero, F J 3DCurator: una herramienta para la inspección de esculturas a través de tomografía computacional Artículo de revista PH: Boletín del Instituto Andaluz del Patrimonio Histórico, (91), 2017, ISSN: 2340-7565. Soler, F; Melero, F J; Luzón, M V A Complete 3D Information System for Cultural Heritage Documentation Artículo de revista Journal of Cultural Heritage, 23 , pp. 49–57, 2017, ISSN: 1296-2074. Bellido-Gant, M L; Melero, F J Atalaya3D: el portal virtual de patrimonio de las universidades andaluzas Artículo de revista PH: Boletín del Instituto Andaluz del Patrimonio Histórico, (90), pp. 15–16, 2016, ISSN: 2340-7565. Martínez, V; Ríos, A M; Melero, F J A Web 3D-Scene Editor of Virtual Reality Exhibitions and 360-degree Videos Artículo en actas Garcia-Alonso, A; Masiá, B (Ed.): Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (CEIG 2016), pp. 9–13, The Eurographics Association, 2016, ISBN: 978-3-03868-023-9. Bolivar, F J; Melero, F J 3DCurator: A 3D Viewer for CTs of Polychromed Wood Sculptures Artículo en actas Garcia-Alonso, A; Masiá, B (Ed.): Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (CEIG 2016), The Eurographics Association, 2016, ISBN: 978-3-03868-023-9. Aguilera, A; Melero, F J; Feito, F Out-of-core real-time haptic interaction on very large models Artículo de revista Computer-Aided Design, 77 , pp. 98–106, 2016, ISSN: 0010-4485. Melero, F J Digitalización 3D del Templo de Millones de Años de Tutmosis III Capítulo de libro Seco, M; Jódar, A (Ed.): pp. 349–365, Editorial de la Universidad de Granada, Granada, 2015, ISBN: 9788433857408. Aguilera, A; Feito, F; Melero, F J EBP-Octree: An Optimized Bounding Volume Hierarchy for Massive Polygonal Models Artículo en actas Juan, M C; Borro, D (Ed.): CEIG - Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (2013), pp. 11–20, The Eurographics Association, 2013, ISBN: 978-84-695-8333-3 . Melero, F J Graphics Systems in a Software Engineering Curriculum Artículo en actas Juan, M C; Borro, D (Ed.): CEIG - Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (2013), pp. 173–176, The Eurographics Association, 2013, ISBN: 978-84-695-8333-3. Contreras, F; Melero, F J; Farjas, M Proceedings of the 38th Annual Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, Granada, Spain, April 2010, Acta de congreso Archaeopress, (2494), 2013, ISBN: 978-1-4073-1108-1. Jiménez, J G; García, M; Revelles, J; Melero, F J Digitalización 3D y Difusión en Web del Patrimonio de las Universidades Andaluzas mediante X3D Y WebGL Artículo de revista Virtual Archaeology Review, 3 (7), pp. 55–59, 2012, ISSN: 1989-9947. Contreras, F; Melero, F J Aplicaciones informáticas en Arqueología (Monográfico) Libro Editorial de la Universidad de Granada, 2011, ISBN: 2174-8063. Melero, F J; Soler, F; Cano, P; Torres, J C Detección de colisiones en grandes modelos geométricos Artículo en actas Actas del XX Congreso Español de Informática Gráfica, CEIG 2010, Ibergarceta Publicaciones SL, Valencia, 2010, ISBN: 978-84-92812-50-9. Melero, F J; León, A; Torres, J C Digitalización y reconstrucción de elementos cerámicos arqueológicos de torno Artículo de revista Virtual Archaeology Review, 1 (2), pp. 137–142, 2010, ISSN: 1989-9947. Torres, J C; Cano, P; Melero, F J; España, M; Moreno, J Aplicaciones de la digitalización 3D del patrimonio Artículo de revista Virtual Archaeology Review, 1 (1), pp. 51-54, 2010, ISSN: 1989-9947. Melero, F J; Cano, P; Revelles, J Fusion of Cultures. Abstracts of the CAA2010 Libro 2010, ISBN: 978-84-693-0772-4. Melero, F J; Soler, F; Cano, P; Torres, J C Real-Time Haptic Rendering on Large Models Artículo en actas Proceedings of the IV Iberoamerican Symposium in Computer Graphics (SIACG'2009), pp. 137–144, Sociedad Venezolana de Computación Gráfica, 2009, ISBN: 978-980-12-3682-5. Melero, F J BP-Octree: Una estructura jerárquica de volúmenes envolventes Tesis doctoral Univ. Granada, 2008, ISBN: 9788469183564. Melero, F J; Cano, P; Torres, J C Bounding-Planes Octree: A New Volume-based LOD Scheme Artículo de revista Computer and Graphics, 32 (4), pp. 385–392, 2008. Melero, F J; Cano, P; Torres, J C Representación multiresolución de sólidos mediante una jerarquía de planos envolventes Capítulo de libro Joan, R; Torres, J C; Feito, F (Ed.): Herramientas Avanzadas en CAD, Capítulo X, Univ. Jaén, 2007, ISBN: 978-84-690-6855-7. Jiménez, M C; Montes, R; Melero, F J Magic Potter Artículo en actas Hernández, L; Flores, J (Ed.): I Simposium de Informática Gráfica y Patrimonio Histórico (SIGPHI), A Coruña, 2007. Melero, F J; Cano, P; Torres, J C Transmisión progresiva de grandes modelos usando una jerarquía de planos envolventes Artículo en actas Cerezo, E; Feito, F (Ed.): XIV Congreso Español de Informática Gráfica (CEIG), Thomson-Paraninfo, Zaragoza, 2007, ISBN: 978-84-9732-595-0. Torres, J C; Melero, F J; Cano, P; Martín, D; León, A Generación automatizada de modelado 3D para difusión y documentación del patrimonio histórico Artículo en actas Hernández, L; Flores, J (Ed.): I Simposium de Informática Gráfica y Patrimonio Histórico (SIGPHI), A Coruña, 2007. Melero, F J; Cano, P; Torres, J C Combining SP-Octrees and impostors for multiresolution visualization Artículo de revista Computer and Graphics, 29 (2), pp. 225–233, 2005, ISSN: 0097-8493. Melero, F J; Cano, P; Torres, J C SP-Octrees visualization using impostors Artículo en actas Alexa, M; Galin, E (Ed.): EUROGRAPHICS 2004 Short Presentations, pp. 81–84, The Eurographics Association 2004, ISSN: 1017-4656. Melero, F J; Cano, P; Torres, J C Visualización interactiva de SP-Octrees utilizando impostores Artículo en actas Congreso Español de Informática Gráfica (CEIG), pp. 119–123, Edicion Digital @Tres, Sevilla, 2004, ISBN: 84-688-6998-8. Melero, F J; León, A; Contreras, F; Torres, J C A new system for interactive vessel reconstruction and drawing Artículo en actas Enter the past. The E-way into the four dimension of cultural heritage. CAA 2003,Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, pp. 78–81, Archaeopress, 2004, ISBN: 1 84171 592 1. Kampel, M; Melero, F J Virtual Vessel Reconstruction from a Fragment s Profile Artículo en actas Arnold, D; Chalmers, A; Niccolucci, F (Ed.): The 4th International Symposium on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Intelligent Cultural Heritage, pp. 79–88, The Eurographics Association, 2003, ISSN: 1811-864X. Melero, F J; Torres, J C; León, A On the Interactive 3D Reconstruction of Iberian Vessels Artículo en actas Arnold, D; Chalmers, A; Niccolucci, F (Ed.): The 4th International Symposium on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Intelligent Cultural Heritage, pp. 71–78, The Eurographics Association, 2003, ISSN: 1811-864X.
2024

title = {Tecnolog\'{i}as digitales aplicadas al patrimonio universitario},
author = {Francisco Javier {Melero}},
editor = {Luis {M\'{e}ndez} and Maria Luisa {Bellido-Gant}},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/2024_IAPH.pdf},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.33349/2024.113.5642},
issn = {2340-7565},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-10},
journal = {Revista PH Instituto Andaluz del Patrimonio Hist\'{o}rico},
volume = {113},
number = {1},
pages = {170-185},
abstract = {El patrimonio universitario es un campo de pruebas ideal para el desarrollo
de soluciones tecnol\'{o}gicas innovadoras. El intercambio de experiencias,
conocimiento y proyectos entre las distintas \'{a}reas del saber que se produce
en los campus universitarios es el caldo de cultivo f\'{e}rtil para aplicar los \'{u}ltimos
avances tecnol\'{o}gicos al patrimonio universitario en su m\'{a}s amplio espectro.
Desde las tecnolog\'{i}as 3D, aplicables a documentaci\'{o}n y divulgaci\'{o}n
de los bienes mueble e inmueble, hasta la vertiginosa disrupci\'{o}n de la
inteligencia artificial en los \'{u}ltimos a\~{n}os, nos encontramos en un contexto
en el que la tecnolog\'{i}a permite incrementar la accesibilidad del patrimonio,
realizar investigaciones novedosas que manejen una mayor cantidad de
datos, o incluso comprender documentos que hasta hace poco resultaban
ininteligibles.
Las universidades, como generadoras y transmisoras del conocimiento
universal, no permanecen ajenas a esta revoluci\'{o}n tecnol\'{o}gica, y pueden
aprovechar estos avances para dar un paso m\'{a}s en la cuarta misi\'{o}n de la
universidad: la difusi\'{o}n del conocimiento y la cultura a trav\'{e}s de la extensi\'{o}n
universitaria. En este art\'{i}culo se hace un somero repaso por gran parte de
estas tecnolog\'{i}as, mostrando casos de uso en contextos universitarios y se
apuntan algunas propuestas de retos y oportunidades que se presentan.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
de soluciones tecnológicas innovadoras. El intercambio de experiencias,
conocimiento y proyectos entre las distintas áreas del saber que se produce
en los campus universitarios es el caldo de cultivo fértil para aplicar los últimos
avances tecnológicos al patrimonio universitario en su más amplio espectro.
Desde las tecnologías 3D, aplicables a documentación y divulgación
de los bienes mueble e inmueble, hasta la vertiginosa disrupción de la
inteligencia artificial en los últimos años, nos encontramos en un contexto
en el que la tecnología permite incrementar la accesibilidad del patrimonio,
realizar investigaciones novedosas que manejen una mayor cantidad de
datos, o incluso comprender documentos que hasta hace poco resultaban
ininteligibles.
Las universidades, como generadoras y transmisoras del conocimiento
universal, no permanecen ajenas a esta revolución tecnológica, y pueden
aprovechar estos avances para dar un paso más en la cuarta misión de la
universidad: la difusión del conocimiento y la cultura a través de la extensión
universitaria. En este artículo se hace un somero repaso por gran parte de
estas tecnologías, mostrando casos de uso en contextos universitarios y se
apuntan algunas propuestas de retos y oportunidades que se presentan.
title = {University heritage and technologies : Current Experiences in Andalucia},
author = {Francisco Javier {Melero} and Maria Luisa {Bellido-Gant} },
editor = {Bernadette Biedermann},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/2024_Musea.pdf},
doi = {https://doi. org/10.25364/32.1:2024.1.12},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-06-01},
journal = {MUSEA. Journal for museology, museum practice and audience},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {160-169},
abstract = {In this text we intend to approach the diverse heritage of the Andalusian universities to understand/analyze the most interesting experiences carried out in the work of diffusion and its relation to information and communication technologies (ICTs). We will analyze the usage of 3D scanning for cataloguing and disseminating movable and immovable artworks, the use of an app and QR codes to access the content, or the immersive experiences of 360° videos to allow connecting heritage with distant people and territories.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2023
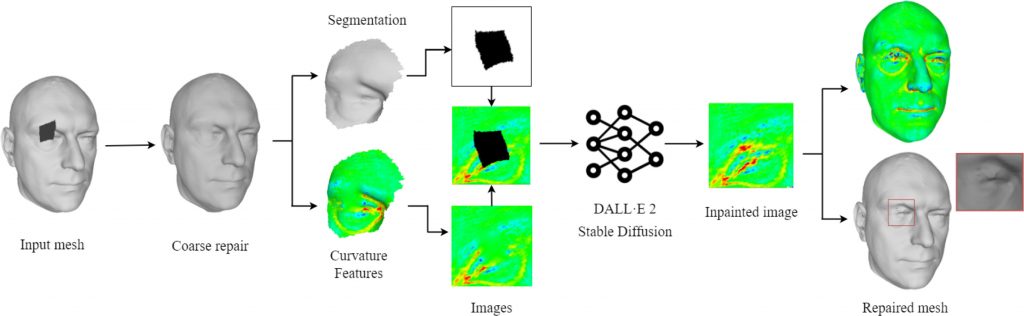
title = {Deep learning of curvature features for shape completion},
author = {Marina {Hern\'{a}ndez-Bautista} and Francisco Javier {Melero}},
editor = {Marc Comino and Jes\'{u}s Gimeno and Ana Serrano},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/2023_CandG_Deep-Learning-of-Curvature-Features-for-Shape-Completion.pdf},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cag.2023.07.007},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-11-01},
journal = {Computers & Graphics},
volume = {115},
pages = {204-215},
abstract = {The paper presents a novel solution to the issue of incomplete regions in 3D meshes obtained through digitization. Traditional methods for estimating the surface of missing geometry and topology often yield unrealistic outcomes for intricate surfaces. To overcome this limitation, the paper proposes a neural network-based approach that generates points in areas where geometric information is lacking. The method employs 2D inpainting techniques on color images obtained from the original mesh parameterization and curvature values. The network used in this approach can reconstruct the curvature image, which then serves as a reference for generating a polygonal surface that closely resembles the predicted one. The paper’s experiments show that the proposed method effectively fills complex holes in 3D surfaces with a high degree of naturalness and detail. This paper improves the previous work in terms of a more in-depth explanation of the different stages of the approach as well as an extended results section with exhaustive experiments.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2021

title = {Ordering Artificial Intelligence Based Recommendations to Tackle the SDGs with a Decision-Making Model Based on Surveys},
author = {Sergio Alonso and Rosana Montes and Daniel Molina and Ivan Palomares and Eugenio Mart\'{i}nez-C\'{a}mara and Manuel Chiach\'{i}o and Juan Chiach\'{i}o and Francisco Javier {Melero} and Pablo {Garc\'{i}a Moral} and B\'{a}rbara Fern\'{a}ndez and Cristina Moral and Rosario Marchena and Javier {P\'{e}rez de Vargas} and Francisco Herrera},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/11/6038},
doi = {10.3390/su13116038},
isbn = {2071-1050},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-06-01},
journal = {Sustainability},
volume = {13},
number = {11},
abstract = {The United Nations Agenda 2030 established 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) as a guideline to guarantee a sustainable worldwide development. Recent advances in artificial intelligence and other digital technologies have already changed several areas of modern society, and they could be very useful to reach these sustainable goals. In this paper we propose a novel decision making model based on surveys that ranks recommendations on the use of different artificial intelligence and related technologies to achieve the SDGs. According to the surveys, our decision making method is able to determine which of these technologies are worth investing in to lead new research to successfully tackle with sustainability challenges.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

title = {Inteligencia Artificial y Tecnolog\'{i}as Digitales para los ODS},
author = {Rosana Montes and Francisco Javier {Melero} and Iv\'{a}n {Palomares} and Sergio Alonso and Juan Chiach\'{i}o and Manuel Chiach\'{i}o and Daniel Molina and Eugenio {Mart\'{i}nez-C\'{a}mara} and Siham Tabik and Francisco Herrera},
url = {https://issuu.com/raing/docs/ia_y_tecnolog_as_digitales_para_los_ods},
year = {2021},
date = {2021-01-11},
publisher = {Real Academia de Ingenier\'{i}a},
abstract = {El libro “Inteligencia Artificial y Tecnolog\'{i}as Digitales para los ODS” (Rosana Montes y coautores, Real Academia de Ingenier\'{i}a, 2021) se organiza en tres partes que se corresponden con la introducci\'{o}n a la inteligencia artificial y las tecnolog\'{i}as digitales, el an\'{a}lisis de su aplicaci\'{o}n en los ODS y se complementa con un conjunto de recomendaciones sobre actuaciones que pueden conducir al desarrollo de proyectos e impulsar el alcance de las metas asociadas. Para ello se ha revisado la literatura cient\'{i}fica especializada considerando m\'{a}s de mil referencias bibliogr\'{a}ficas en torno las 169 metas que se plantean para alcanzar los ODS.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {book}
}
2020

title = {Consulting the oracle: Can data mining over GEM Dataset tell something about unemployed entrepreneurs?},
author = {Francisco Javier {Melero} and M.M. {Fuentes}},
editor = {Loreto {Fern\'{a}ndez Fern\'{a}ndez} and Isabel {Neira G\'{o}mez} and Sara {Fern\'{a}ndez L\'{o}pez}},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/2020_GEMCEE_extracto.pdf},
isbn = {978-84-09-23683-1},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-09-10},
booktitle = {V Workshop Internacional de Investigaci\'{o}n en Emprendimiento GEM-ACEDE},
pages = {45-48},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {workshop}
}
title = {Nuevas tecnolog\'{i}as para la documentaci\'{o}n y difusi\'{o}n del patrionio cofrade},
author = {F.J. Melero},
editor = {F.J. Crespo
J.M. Valverde},
year = {2020},
date = {2020-02-22},
booktitle = {La Semana Santa de Granada: Pasado, presente y futuro},
pages = {151-191},
publisher = {Ed. Nuevo Inicio},
address = {Granada},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
2019
title = {Atalaya3D: Disseminating Andalusian Public Universities’ Heritage through 3D and Web Technologies},
author = {Francisco Javier {Melero} and Manuela Garcia and Maria Luisa {Bellido-Gant} },
url = {http://umac.icom.museum/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/UMACJ_11-1_2019.pdf},
issn = {2071-7229},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-09-04},
journal = {University Museums and Collections Journal (UMACJ)},
volume = {11},
number = {1},
pages = {43},
abstract = {Andalusia is an autonomous region in southern Spain with 10 public universities, of which two date back to the 16th century: the University of Seville (1505) and the University of Granada (1531). Some have all their buildings and offices in a single campus, such as the University of Almeria and the
University of Huelva, while others are distributed among several campuses in a city or even in several cities separated by hundreds of kilometers. We can thus consider the cultural heritage of Andalusian universities to be a geographically distributed collection, impossible to visit in one go. In this paper, we will present and discuss Atalaya3D, a collaborative project that aims to make this cultural heritage accessible to the public. It consists of a virtual platform (web and app) that uses the most recent advances in the field of 3D scanning, 3D web displays and a mobile app to enable the exploration of these institutions’ vast heritage in a 3D environment before (or without) visiting the campus. Since 2010, more than one hundred artworks and historical buildings have been accurately scanned using the latest 3D scanning and photogrammetric technologies resulting in, not only the promotion of the university heritage to large audiences, but also in the precise documentation of geometry, architecture and color. In-place visitors can obtain a better experience by obtaining extra information from the mobile app, easily triggered by reading QR codes. Moreover, the usage of social media expands and disseminates the advances, results, and contents of the project. },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
University of Huelva, while others are distributed among several campuses in a city or even in several cities separated by hundreds of kilometers. We can thus consider the cultural heritage of Andalusian universities to be a geographically distributed collection, impossible to visit in one go. In this paper, we will present and discuss Atalaya3D, a collaborative project that aims to make this cultural heritage accessible to the public. It consists of a virtual platform (web and app) that uses the most recent advances in the field of 3D scanning, 3D web displays and a mobile app to enable the exploration of these institutions’ vast heritage in a 3D environment before (or without) visiting the campus. Since 2010, more than one hundred artworks and historical buildings have been accurately scanned using the latest 3D scanning and photogrammetric technologies resulting in, not only the promotion of the university heritage to large audiences, but also in the precise documentation of geometry, architecture and color. In-place visitors can obtain a better experience by obtaining extra information from the mobile app, easily triggered by reading QR codes. Moreover, the usage of social media expands and disseminates the advances, results, and contents of the project. 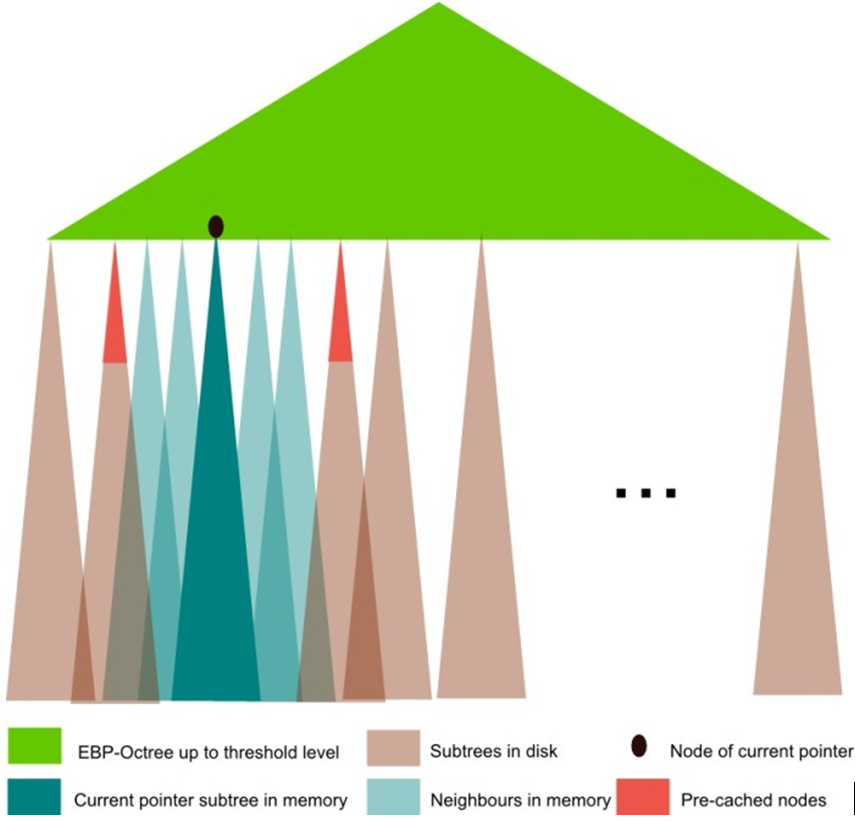
title = {Fast collision detection between high resolution polygonal models},
author = {F.J. Melero and A. Aguilera and F. Feito
},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/melero_cg2019.pdf},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cag.2019.07.006},
issn = {0097-8493},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-07-25},
journal = {Computers & Graphics},
volume = {83},
pages = {97-106},
abstract = {In this paper, we address the problem of collision detection between very high resolution polygonal models. We propose an approach that uses the EBP-Octree data structure in a single-core CPU architecture. The algorithm manages a set of files to support a cache-like out-of-core algorithm that performs the collision and intersection tests. Our method uses a data structure called EBP-Octree (Extended Bounding-Planes Octree), which is a very tight hierarchy of convex bounding volumes that, based on a spatial decomposition of the model using an octree, defines a bounding volume at each node by a subset of the planes of the portion of polygonal model contained at that node. The system adapts the memory consumption to the system’s hardware features so it can provide exact triangle collision detection in almost any environment, since the amount of information in the main memory can be limited just varying the threshold of the EBP-Octree. We have tested the data structure and the algorithm in scenarios where two models of 28 million polygons move through one another, achieving real time frame rates for first collision tests on a commonly available computer.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2018

title = {Atalaya3D: Making Universities' Cultural Heritage Accessible Through 3D Technologies},
author = {Francisco Javier Melero and Jorge Revelles and Maria Luisa Bellido},
editor = {Robert Sablatnig and Michael Wimmer},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/meleroRevellesBellido18.pdf},
doi = {10.2312/gch.20181338},
issn = {2312-6124},
year = {2018},
date = {2018-01-01},
booktitle = {Eurographics Workshop on Graphics and Cultural Heritage},
pages = {31-35},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
abstract = {This work was carried out over the past eight years through the Atalaya3D project, which aims to make the cultural heritage of the ten public Andalusian universities accessible. Since 2010, the project has been a pioneer in the field of 3D scanning of sculptures and historical sites, opening up restricted areas virtually through 3D web displays. Moreover, in addition to the website, a mobile app allows visitors to browse these institutions’ vast heritage and examine it before visiting the campus in a 3D environment. More than 70 artworks and historical buildings have been accurately scanned using the latest 3D scanning technologies, so that we now have the geometry and colour of the pieces documented in detail. QR codes make it easier to reach the relevant information about our universities’ heritage via any mobile device (phone or tablet).},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2017

title = {CEIG 2017. Proceedings of the XXVII Spanish Computer Graphics Conference },
author = {Melero, F.J. and Pelechano, N.},
editor = {Melero, F.J. and Pelechano, N.},
url = {https://diglib.eg.org:443/handle/10.2312/ceig20172016},
doi = {10.2312/ceig.20172016 },
isbn = {978-3-03868-046-8},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-06-02},
booktitle = {Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (CEIG 2017)},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
address = {Sevilla},
organization = {Eurographics Secci\'{o}n Espa\~{n}ola, EGSE},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
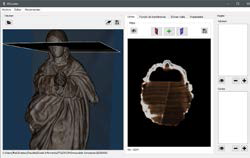
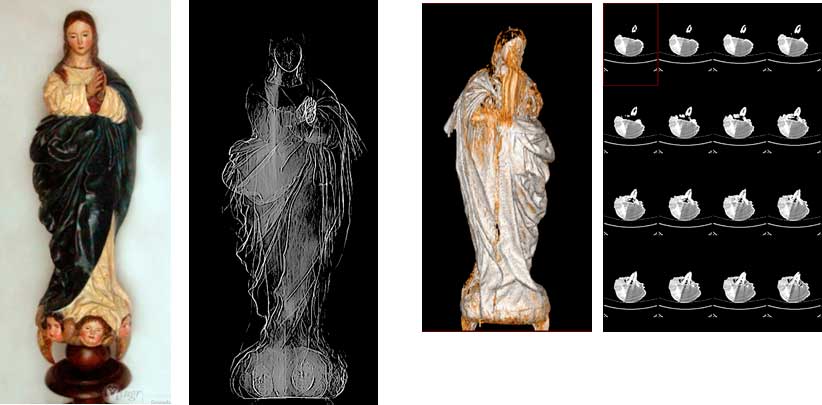
title = {3DCurator: una herramienta para la inspecci\'{o}n de esculturas a trav\'{e}s de tomograf\'{i}a computacional},
author = {Bol\'{i}var, F.J. and Melero, F.J. },
url = {http://www.iaph.es/revistaph/index.php/revistaph/article/download/3906/3889},
issn = {2340-7565},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-04-07},
journal = {PH: Bolet\'{i}n del Instituto Andaluz del Patrimonio Hist\'{o}rico},
number = {91},
abstract = {3DCurator se ha desarrollado para permitir el examen 3D del interior de esculturas no met\'{a}licas. Actualmente el software disponible en el mercado para el an\'{a}lisis de estos datos est\'{a} orientado a la medicina y es, adem\'{a}s de complejo, generalmente caro. Por este motivo se ha trabajado en la creaci\'{o}n de una herramienta sencilla, configurada inicialmente para la visualizaci\'{o}n \'{o}ptima del interior de esculturas de madera, con la que los restauradores e investigadores del arte puedan explorar sin generar cortes y tomen medidas sin que exista riesgo de da\~{n}ar, en ning\'{u}n momento, la figura examinada.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

title = {A Complete 3D Information System for Cultural Heritage Documentation},
author = {Soler, F. and Melero, F.J. and Luz\'{o}n, M.V.},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2016.09.008},
doi = {10.1016/j.culher.2016.09.008},
issn = {1296-2074},
year = {2017},
date = {2017-01-12},
journal = {Journal of Cultural Heritage},
volume = {23},
pages = {49--57},
abstract = {Cultural heritage (CH) documentation tasks usually involve professionals from different knowledge areas, which implies not only a huge amount of information and requirements, but also a very heterogeneous set of sources, data structures, content and formats. Geographic information systems (GIS) have been used extensively by cultural heritage specialists, but this is just working around the real problem: there is no specialized software for CH professionals to document their work in 3D. In this paper, we present software named Agata that allows specialists to interact in real time with high resolution polygonal models, and to annotate different raster and vectorial information directly onto them that might be useful for current or future research. Moreover, these annotations can be exported in a standard format that allows researchers from other disciplines that might be interested in the dataset to access such information easily. The system is able to manage and annotate not only on buildings or archaeological sites, but also sculptures or paintings directly into the 3D dataset of any CH physical element.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2016
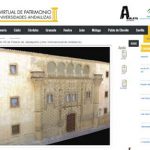
title = {Atalaya3D: el portal virtual de patrimonio de las universidades andaluzas},
author = {Bellido-Gant, M.L. and Melero, F.J.},
url = {http://www.iaph.es/revistaph/index.php/revistaph/article/view/3809/3824},
issn = {2340-7565},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-10-15},
journal = {PH: Bolet\'{i}n del Instituto Andaluz del Patrimonio Hist\'{o}rico},
number = {90},
pages = {15--16},
abstract = {En el marco del Observatorio Atalaya, los Vicerrectorados de Extensi\'{o}n y Cultura de las universidades p\'{u}blicas andaluzas, conscientes del variado y rico patrimonio cultural que atesoran, impulsaron el proyecto de Portal Virtual de Patrimonio de las Universidades Andaluzas, coordinado por la Universidad de Granada, con el fin de conseguir la difusi\'{o}n del mismo y su puesta en valor y visibilizaci\'{o}n. Actualmente es una plataforma Web mediante la que cualquier navegante puede acceder a informaci\'{o}n textual y gr\'{a}fica de las principales obras del patrimonio de las diez universidades p\'{u}blicas de Andaluc\'{i}a.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
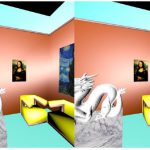
title = {A Web 3D-Scene Editor of Virtual Reality Exhibitions and 360-degree Videos},
author = {Mart\'{i}nez, V. and R\'{i}os, A.M and F.J. Melero
},
editor = {Garcia-Alonso, A. and Masi\'{a}, B.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/exhibitions360-fin.pdf
https://diglib.eg.org/handle/10.2312/ceig20161308},
doi = {10.2312/ceig.20161308 },
isbn = {978-3-03868-023-9},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-08-24},
booktitle = {Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (CEIG 2016)},
pages = {9--13},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
abstract = {This work consists in the development of a Web-based system which allows museum managers to generate their own virtual 3D exhibitions, using a two-dimensional graphical user interface. These virtual 3D exhibitions can be displayed interactively in the museum's website, or as a immersive experience in a virtual headset (e.g. Google CardBoard) via a mobile app. We use the SVG specification to edit the exhibition, handling 3D models of the rooms, sculptures and pictures. Furthermore, the user can add to the scene a list of cameras with their respective control points, and then generate several routes through the scene. The scene is rendered in the browser using standard technologies, such as WebGL (ThreeJS) and X3D (X3DOM), and the mobile app is generated via Unity3D . Also, the X3D and MPEG-4 compression standards allow us to transform the scene and its camera routes into 360 videos, where user can manipulate camera orientation while playing the track. Also, audio tracks can be added to each route and hence, inserted in the 360-degree video.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

title = {3DCurator: A 3D Viewer for CTs of Polychromed Wood Sculptures},
author = {F.J. Bolivar and F.J. Melero},
editor = {Garcia-Alonso, A. and Masi\'{a}, B.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/3dcurator-fin.pdf
https://diglib.eg.org:443/handle/10.2312/ceig20161311},
doi = {10.2312/ceig.20161311 },
isbn = {978-3-03868-023-9},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-05-20},
booktitle = {Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (CEIG 2016)},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
abstract = {We present in this work a new software designed for the 3D documentation of wood sculptures from computer tomography (CT) datasets. The system provides rendering presets and tools that allow the experts to examine the artwork in a more confident and exhaustive manner than using the traditional bidimensional X-ray plate. Most of current available volume rendering tools are very expensive and oriented towards medical datasets, which makes unusable by art curators due to its price and its humanfocused rendering options. We have developed a new system that loads DICOM files and performs rendering operations and several documentation actions, such as taking measurements or extracting slices at any orientation.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
title = {Out-of-core real-time haptic interaction on very large models},
author = {Aguilera, A. and Melero, F.J. and Feito, F.
},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010448516300148},
doi = {10.1016/j.cad.2016.04.002},
issn = { 0010-4485},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-04-11},
journal = {Computer-Aided Design},
volume = {77},
pages = {98--106},
abstract = {In this paper we address the problem of fast inclusion tests and distance calculation in very large models, an important issue in the context of environments involving haptic interaction or collision detection. Unfortunately, existing haptic rendering or collision detection toolkits cannot handle polygonal models obtained from 3D digitized point clouds unless the models are simplified up to a few thousand polygons, which leads to an important lack of detail for the scanned pieces. We propose a data structure that is able to manage very large polygonal models (over 25M polygons), and we explain how this can be used in order to compute the inclusion of a point into the solid surface very efficiently, performing several thousand point-in-solid tests per second. Our method uses a data structure called EBP-Octree (Extended Bounding-Planes Octree), which is a very tight hierarchy of convex bounding volumes. Based on a spatial decomposition of the model using an octree, at each node it defines a bounding volume using a subset of the planes of the portion of the polygonal model contained at that node. We use the EBP-Octree in a haptic interaction environment, where distance tests and the orientation of collided triangles must be accurate and fast. We also demonstrate that the proposed algorithm largely meets the interactive query rate demanded by a haptic interaction (1 kHz), despite being executed in a single CPU thread on a commonly available computer.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2015
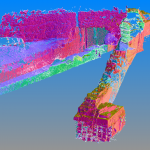
title = {Digitalizaci\'{o}n 3D del Templo de Millones de A\~{n}os de Tutmosis III},
author = {Melero, F.J. },
editor = {Seco, M. and J\'{o}dar, A.},
isbn = {9788433857408},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-08-28},
pages = {349--365},
publisher = {Editorial de la Universidad de Granada},
address = {Granada},
abstract = {This paper presents the first stages and preliminary results of the 3D documentation of the Mortuary Temple of Thutmosis III. By using a 3D laser scanner, on 2012 it was performed a complete survey of the surface and discovered tombs, obtaining more than four billion points that are being processed to get a complete 3D model of the excavation. This accurate three-dimensional model will allow enhancing and facilitating further works not only from pure archaeological researchers, but also from auxiliary sciences, like geophysics.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
2013

title = {EBP-Octree: An Optimized Bounding Volume Hierarchy for Massive Polygonal Models},
author = {Aguilera, A. and Feito, F. and Melero, F.J. },
editor = {Juan, M.C. and Borro, D.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/2013_CEIG.pdf},
isbn = {978-84-695-8333-3 },
year = {2013},
date = {2013-09-01},
booktitle = {CEIG - Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (2013)},
pages = {11--20},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
abstract = {This paper presents a data structure to efficiently handle a hierarchy of bounding volumes on massive polygonal models, such as those obtained from 3D scanning devices. The Extended Bounding-Planes Octree (EBP-Octree) is able to manage massive polygonal models by using a spatial indexation of the surface and storing a hierarchy of bounding volumes composed of planes from the original surface. In this work we detail the geometric and design criteria that have been considered in order to create, just once for each model, an out-of-core data structure that will be dynamically loaded in run-time while traversing the octree in environments such as collision detections of progressive transmission. Due to the applications that might use this data structure, the main goals are to obtain a tight volume at each node and a fast transition among disk and main memory while loading and releasing the octree branches.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
title = {Graphics Systems in a Software Engineering Curriculum},
author = {Melero,F.J. },
editor = {Juan, M.C. and Borro, D. },
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/2013_CEIG_edu.pdf},
isbn = {978-84-695-8333-3},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-09-01},
booktitle = {CEIG - Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (2013)},
pages = {173--176},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
abstract = {In this paper we describe the approach taken to integrate in a quite natural manner the development of graphics systems into the Software Engineering specialization branch of the new degree in Computer Engineering. Given the fact that Computer Graphics is a mandatory course for all students of any of the branches, the Graphics Systems course is more oriented towards a high level design and programming of software and to serve as a basis for other existing optional courses (e.g. Animation, Game Programming, Human-Computer Interaction, etc.).
The approach taken during the first year of this course has been quite successful given the results of the survey passed to students before the end of the semester and hence before the qualifications. The lab works of the whole semester have been pivoting around the same problem, a solar system, and it has been developed using different technologies.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
The approach taken during the first year of this course has been quite successful given the results of the survey passed to students before the end of the semester and hence before the qualifications. The lab works of the whole semester have been pivoting around the same problem, a solar system, and it has been developed using different technologies.

title = {Proceedings of the 38th Annual Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, Granada, Spain, April 2010,},
author = {Contreras, F. and Melero, F.J. and Farjas, M.},
isbn = {978-1-4073-1108-1},
year = {2013},
date = {2013-03-01},
number = {2494},
publisher = {Archaeopress},
series = {BAR International Series},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
2012

title = {Digitalizaci\'{o}n 3D y Difusi\'{o}n en Web del Patrimonio de las Universidades Andaluzas mediante X3D Y WebGL},
author = {Jim\'{e}nez, J.G. and Garc\'{i}a, M. and Revelles, J. and Melero, F.J. },
url = {https://polipapers.upv.es/index.php/var/article/view/4386/4512},
doi = {10.4995/var.2012.4386},
issn = {1989-9947},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-11-16},
journal = {Virtual Archaeology Review},
volume = {3},
number = {7},
pages = {55--59},
abstract = {Under the auspices of the Atalaya Project we have digitalized a set of artworks and historical rooms that belong to the Cultural Heritage of andalusian universities. In a first phase we have scanned with submillimetric accuracy 24 sculptures from Universities of Seville and Granada, as well as seven historical rooms of the latter, obtaining models that have from 70 to 240 million polygons. These datasets have been used in the newly-created website about the Cultural Heritage of the Andalusian Universities, where visitors can visualize not only text, photographs and videos, but also can examine in real 3D the scanned sculptures, and even perform walkthroughs inside the scanned rooms without any need of installing external plugins, by having used in its development standards such as X3D and WebGL.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2011

title = {Aplicaciones inform\'{a}ticas en Arqueolog\'{i}a (Monogr\'{a}fico)},
author = {Contreras, F. and Melero, F.J. },
url = {http://revistaseug.ugr.es/index.php/cpag/issue/view/12},
isbn = {2174-8063},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-07-21},
journal = {Cuadernos de Prehistoria y Arqueolog\'{i}a},
volume = {20},
pages = {502},
publisher = {Editorial de la Universidad de Granada},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {book}
}
2010
title = {Detecci\'{o}n de colisiones en grandes modelos geom\'{e}tricos},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Soler, F. and Cano, P. and Torres, J.C. },
isbn = {978-84-92812-50-9},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-09-02},
booktitle = {Actas del XX Congreso Espa\~{n}ol de Inform\'{a}tica Gr\'{a}fica, CEIG 2010},
publisher = {Ibergarceta Publicaciones SL},
address = {Valencia},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
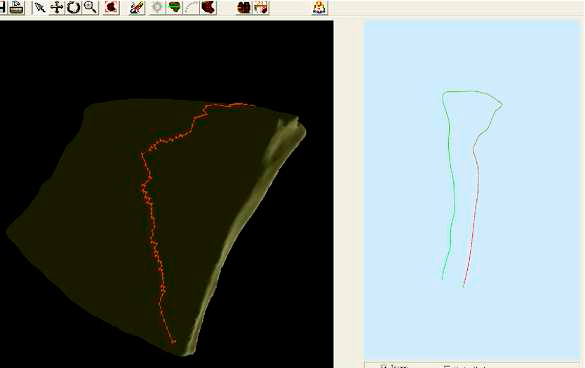
title = {Digitalizaci\'{o}n y reconstrucci\'{o}n de elementos cer\'{a}micos arqueol\'{o}gicos de torno},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Le\'{o}n, A. and Torres, J.C. },
url = {https://polipapers.upv.es/index.php/var/article/view/4716/4869},
doi = {10.4995/var.2010.4716},
issn = {1989-9947},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-05-01},
journal = {Virtual Archaeology Review},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {137--142},
abstract = {Many researchers have dealt during last decade about digitizing and reconstructing hand made pottery elements from fragments retrieved in the archaeological excavations. Some studies have demonstrated the huge variability in results from manual processes, which usually leads into a wrong typological classification of the profile. Moreover, after orienting the fragment, the final document is usually a bi-dimensional picture displaying several measurements and without any well defined standard with respect to appearance. In this paper we present a survey of those techniques that have been developed by our group and we raise some questions and challenges that still have to be solved.
},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
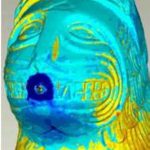
title = {Aplicaciones de la digitalizaci\'{o}n 3D del patrimonio},
author = {Torres, J.C. and Cano, P. and Melero, F.J. and Espa\~{n}a, M. and Moreno, J.},
url = {https://polipapers.upv.es/index.php/var/article/view/4768/4902},
doi = {10.4995/var.2010.4768},
issn = {1989-9947},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-04-01},
journal = {Virtual Archaeology Review},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {51-54},
abstract = {3D digitalization has become a common tool in archaeology. However, the post processing of the data produced by the scanners is still quite complex, and the computer models generated are given very few practical applications.
In this paper, we analyse the key steps involved in the processing of the point clouds. We also review some of the more usual applications for the digital models and propose a conceptual framework for the use of this models in the documentation of cultural heritage.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
In this paper, we analyse the key steps involved in the processing of the point clouds. We also review some of the more usual applications for the digital models and propose a conceptual framework for the use of this models in the documentation of cultural heritage.
title = {Fusion of Cultures. Abstracts of the CAA2010},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Cano, P. and Revelles, J.},
isbn = {978-84-693-0772-4},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-03-30},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {book}
}
2009

title = {Real-Time Haptic Rendering on Large Models},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Soler, F. and Cano, P. and Torres, J.C.},
isbn = {978-980-12-3682-5},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-08-05},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IV Iberoamerican Symposium in Computer Graphics (SIACG'2009)},
pages = {137--144},
publisher = {Sociedad Venezolana de Computaci\'{o}n Gr\'{a}fica},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2008

title = {BP-Octree: Una estructura jer\'{a}rquica de vol\'{u}menes envolventes},
author = {Melero, F.J.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/17693895.pdf},
isbn = {9788469183564},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-11-24},
school = {Univ. Granada},
abstract = {El BP-Octree, Bounding-Planes Octree, es un esquema de representaci\'{o}n que permite la descripci\'{o}n de s\'{o}lidos mediante una jerarqu\'{i}a octal de vol\'{u}menes envolventes definidos en cada nodo por la intersecci\'{o}n de semiespacios planos. Esta estructura se construye siguiendo un algoritmo ascendente por el \'{a}rbol octal, y hace uso de un algoritmo de clustering, el k-medoides, para la \'{o}ptima selecci\'{o}n de los planos envolventes en cada uno de los nodos.
Esta estructura de datos permite la visualizaci\'{o}n progresiva y adaptativa de grandes modelos poligonales, haciendo uso de impostores dependientes del observador para la mejora de la calidad visual.
Adem\'{a}s, el BP-Octree hace uso de un eficiente algoritmo de indexaci\'{o}n espacial y de navegaci\'{o}n por el octree de forma que se consiguen ratios de refresco en aplicaciones de interacci\'{o}n h\'{a}pticas por encima de un mill\'{o}n de tests por segundo. },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
Esta estructura de datos permite la visualización progresiva y adaptativa de grandes modelos poligonales, haciendo uso de impostores dependientes del observador para la mejora de la calidad visual.
Además, el BP-Octree hace uso de un eficiente algoritmo de indexación espacial y de navegación por el octree de forma que se consiguen ratios de refresco en aplicaciones de interacción hápticas por encima de un millón de tests por segundo. 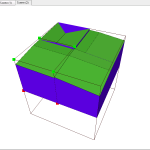
title = {Bounding-Planes Octree: A New Volume-based LOD Scheme},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Cano, P. and Torres, J.C.},
editor = {Jorge, J.A.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/cg08_melero.pdf},
doi = {10.1016/j.cag.2008.04.008},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-01-01},
journal = {Computer and Graphics},
volume = {32},
number = {4},
pages = {385--392},
publisher = {Elsevier},
abstract = {In this paper we present a new data structure: the BP-Octree (Bounding-planes Octree). The BP-Octree is based on a spatial decomposition of the model using an octree, and offers a very tight hierarchy of convex bounding volumes which leads to simplified models. It is done by assigning to each node of the tree a set of planes that, intersected one among others, creates a bounding volume of the part of the model contained in that node. These planes are taken from the real polygons of the model, and are selected at each level guaranteeing that they include completely all boundings of deeper levels.
By using this scheme, it is possible to achieve several tasks apart from the inherent collision detection algorithms, such as the progressive transmission of the bounding volume by sending the planes coefficients needed at each level\textemdashjust the index of each plane if it has been previously transmitted. On the client side, the visualization algorithm is responsible for reconstructing the polygonal geometry from the set of planes just applying a mesh clipping algorithm.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
By using this scheme, it is possible to achieve several tasks apart from the inherent collision detection algorithms, such as the progressive transmission of the bounding volume by sending the planes coefficients needed at each level—just the index of each plane if it has been previously transmitted. On the client side, the visualization algorithm is responsible for reconstructing the polygonal geometry from the set of planes just applying a mesh clipping algorithm.
2007
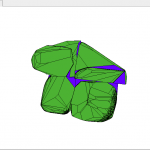
title = {Representaci\'{o}n multiresoluci\'{o}n de s\'{o}lidos mediante una jerarqu\'{i}a de planos envolventes},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Cano, P. and Torres, J.C.},
editor = {Joan, R. and Torres, J.C. and Feito, F.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/shacad_melero.pdf},
isbn = {978-84-690-6855-7},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
booktitle = {Herramientas Avanzadas en CAD},
publisher = {Univ. Ja\'{e}n},
chapter = {X},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inbook}
}
title = {Magic Potter},
author = {Jim\'{e}nez, M.C. and Montes, R. and Melero, F.J.},
editor = {Hern\'{a}ndez, L. and Flores, J.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/melero07b.pdf},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
booktitle = {I Simposium de Inform\'{a}tica Gr\'{a}fica y Patrimonio Hist\'{o}rico (SIGPHI)},
address = {A Coru\~{n}a},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

title = {Transmisi\'{o}n progresiva de grandes modelos usando una jerarqu\'{i}a de planos envolventes},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Cano, P. and Torres, J.C.},
editor = {Cerezo, E. and Feito, F.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/fjmelero_cedi2007.pdf},
isbn = { 978-84-9732-595-0},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
booktitle = {XIV Congreso Espa\~{n}ol de Inform\'{a}tica Gr\'{a}fica (CEIG)},
publisher = {Thomson-Paraninfo},
address = {Zaragoza},
abstract = {En este art\'{i}culo presentamos una nueva estructura de datos que permite transmitir y visualizar a traves de la red grandes modelos tridimensionales. Esta estructura, denominada BP-Octree (Bounding-Planes Octree) est\'{a} basa en la descomposici\'{o}n espacial del modelo usando un octree, asignando a cada nodo del \'{a}rbol un conjunto de planos que forman un volumen envolvente de la parte del modelo contenido en dicho nodo. Estos planos son obtenidos de los pol\'{i}gonos reales del modelo, y se seleccionan en cada nivel garantizando que engloban totalmente a los vol\'{u}menes englobados por los planos seleccionados en los nodos hijos.
Usando esta representaci\'{o}n, la transmisi\'{o}n del modelo a trav\'{e}s de la red no se realiza por pol\'{i}gonos, sino que se env\'{i}an los planos que se necesitan para la visualizaci\'{o}n en cada momento, o sus \'{i}ndices si
ya han sido previamente usados. El algoritmo de visualizaci\'{o}n de la parte cliente se encarga de realizar la extracci\'{o}n de la geometr\'{i}a correspondiente mediante un simple algoritmo de recorte de mallas.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Usando esta representación, la transmisión del modelo a través de la red no se realiza por polígonos, sino que se envían los planos que se necesitan para la visualización en cada momento, o sus índices si
ya han sido previamente usados. El algoritmo de visualización de la parte cliente se encarga de realizar la extracción de la geometría correspondiente mediante un simple algoritmo de recorte de mallas.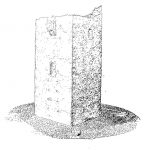
title = {Generaci\'{o}n automatizada de modelado 3D para difusi\'{o}n y documentaci\'{o}n del patrimonio hist\'{o}rico},
author = {Torres, J.C. and Melero, F.J. and Cano, P. and Mart\'{i}n, D. and Le\'{o}n, A.},
editor = {Hern\'{a}ndez, L. and Flores, J.},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-01-01},
booktitle = {I Simposium de Inform\'{a}tica Gr\'{a}fica y Patrimonio Hist\'{o}rico (SIGPHI)},
address = {A Coru\~{n}a},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2005
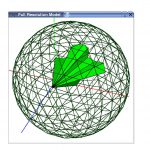
title = {Combining SP-Octrees and impostors for multiresolution visualization},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Cano, P. and Torres, J.C.},
editor = {Jorge, J.A.},
url = {http://hera.ugr.es/doi/15771866.pdf},
doi = {10.1016/j.cag.2004.12.008},
issn = {0097-8493},
year = {2005},
date = {2005-01-01},
journal = {Computer and Graphics},
volume = {29},
number = {2},
pages = {225--233},
abstract = {Space-Partition Octree (SP-Octree) is a hierarchical representation scheme for solid modelling. It allows a multiresolution representation of polyhedral objects, and has been successfully used in progressive transmission. Moreover, this scheme allows visualising the model in an adaptive way. However, at intermediate levels of the SP-Octree, the obtained visualisation is a rough approximation of the object due to the fact that grey nodes are approximated by the face's planes belonging to the convex hull of the solid included in that node.
In this paper, we present an approach that improves the visualisation of these multiresolution SP-Octrees models by applying impostors over those planes that are not part of the solid boundary. This way, it is possible to obtain a more realistic visualisation of the object, although the maximum LOD is not used. At each moment, the impostor is selected depending on the observer's viewpoint. Each SP-Octree has associated a set of impostors that are views of the modelled complex solid.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
In this paper, we present an approach that improves the visualisation of these multiresolution SP-Octrees models by applying impostors over those planes that are not part of the solid boundary. This way, it is possible to obtain a more realistic visualisation of the object, although the maximum LOD is not used. At each moment, the impostor is selected depending on the observer's viewpoint. Each SP-Octree has associated a set of impostors that are views of the modelled complex solid.
2004
title = {SP-Octrees visualization using impostors},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Cano, P. and Torres, J.C.},
editor = {Alexa, M. and Galin, E.},
url = {https://diglib.eg.org/handle/10.2312/egs20041008},
doi = {10.2312/egs.20041008},
issn = {1017-4656},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-09-02},
booktitle = {EUROGRAPHICS 2004 Short Presentations},
pages = {81--84},
organization = {The Eurographics Association},
series = {Eurographics technical report series},
abstract = {SP-Octrees (Space-Partition Octrees) allow a multiresolution representation of polyhedral objects, and have been successfully used in progressive transmission. Nonetheless, the SP-Octree is a solid modeling structure, intended to solve problems as solid intersections and point inclusion tests. At intermediate levels of the SP-Octree, the visualization is a rough approximation of the object due to the fact that grey nodes are shown as the convex hull of the part of the solid included in that node.
In this paper we present an approach to use SP-Octrees for adaptative visualization, that improves the visualization of these multiresolution models by applying impostors over those planes of the hierarchical structure that belongs to the convex hull but are not part of the solid boundary (ficticious planes). By doing so, it is possible to obtain a better approximating visualization of the object, although the maximum LOD is not used. At every moment, the impostor is selected depending on the viewpoint.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
In this paper we present an approach to use SP-Octrees for adaptative visualization, that improves the visualization of these multiresolution models by applying impostors over those planes of the hierarchical structure that belongs to the convex hull but are not part of the solid boundary (ficticious planes). By doing so, it is possible to obtain a better approximating visualization of the object, although the maximum LOD is not used. At every moment, the impostor is selected depending on the viewpoint.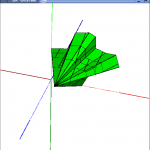
title = {Visualizaci\'{o}n interactiva de SP-Octrees utilizando impostores},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Cano, P. and Torres, J.C.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/melero_cano_torres.pdf},
isbn = {84-688-6998-8},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-07-01},
booktitle = {Congreso Espa\~{n}ol de Inform\'{a}tica Gr\'{a}fica (CEIG)},
pages = {119--123},
publisher = {Edicion Digital @Tres},
address = {Sevilla},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
title = {A new system for interactive vessel reconstruction and drawing},
author = {Melero,F.J. and Le\'{o}n, A. and Contreras, F. and Torres, J.C. },
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/CD10_Melero_et_al_CAA_2003.pdf},
isbn = {1 84171 592 1},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-04-09},
booktitle = {Enter the past. The E-way into the four dimension of cultural heritage. CAA 2003,Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology},
journal = {Bar International Series},
volume = {1227},
pages = {78--81},
publisher = {Archaeopress},
abstract = {We present an easy, automatic and efficient full vessel reconstruction and drawing system, which works using a mesh model of the fragment taken from a 3D scanner.
To get the appropriate orientation, the archaeologist selects some areas of the border. A genetic algorithm is then applied to the points on these areas obtaining the plane that best fits the border of the fragment.
The profile of the vessel is also interactively chosen by the expert, who draws it on the fragment as in a graphical editor. This profile is also editable, it being possible to eliminate, move or insert points. From this information, the system generates the unknown part of the profile using splines. Finally, the system makes it possible to create a 3D virtual view of the complete vessel and the traditional 2D drawing, such that it can be edited (i.e. by positioning the original fragment or placing measurement lines).
The software is very efficient, enabling the creation of the drawings in a few minutes.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
To get the appropriate orientation, the archaeologist selects some areas of the border. A genetic algorithm is then applied to the points on these areas obtaining the plane that best fits the border of the fragment.
The profile of the vessel is also interactively chosen by the expert, who draws it on the fragment as in a graphical editor. This profile is also editable, it being possible to eliminate, move or insert points. From this information, the system generates the unknown part of the profile using splines. Finally, the system makes it possible to create a 3D virtual view of the complete vessel and the traditional 2D drawing, such that it can be edited (i.e. by positioning the original fragment or placing measurement lines).
The software is very efficient, enabling the creation of the drawings in a few minutes.
2003
title = {Virtual Vessel Reconstruction from a Fragment s Profile},
author = {Kampel, M. and Melero, F.J.},
editor = {Arnold, D. and Chalmers, A. and Niccolucci, F.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/079-088.pdf},
doi = {10.2312/VAST/VAST03/079-088},
issn = {1811-864X},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
booktitle = {The 4th International Symposium on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Intelligent Cultural Heritage},
pages = {79--88},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
abstract = {Every archaeological excavation must deal with a vast number of ceramic fragments. The documentation, administration and scientific processing of these fragments represent a temporal, personnel, and financial problem. Up to now documentation and classification have been done manually which means a lot of routine work for archaeologists and a very inconsistent representation of the real object. First, there may be errors in the measuring process (diameter or height may be inaccurate). Second, the drawing of the fragment should be in a consistent style, which is not possible since a drawing of an object without interpreting it is very hard to do. We are developing a documentation system for archaeological fragments based on their profile, which is the cross-section of the fragment in the direction of the rotational axis of symmetry. Hence the position of a fragment (orientation) on a vessel is important, since it allows a good profile to be obtained. This paper presents two different approaches to the estimation of the orientation of archaeological fragments and the profile extraction. One method is based on a Hough inspired approach and the other is based on genetic algorithms and expert interaction. We compare the methods and show results with respect to robustness, applicability, and accuracy.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
title = {On the Interactive 3D Reconstruction of Iberian Vessels},
author = {Melero, F.J. and Torres, J.C and Le\'{o}n, A. },
editor = {Arnold, D. and Chalmers, A. and Niccolucci, F.},
url = {https://lsi2.ugr.es/fjmelero/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/071-078.pdf},
doi = {10.2312/VAST/VAST03/071-078},
issn = {1811-864X},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
booktitle = {The 4th International Symposium on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Intelligent Cultural Heritage},
pages = {71--78},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Publicaciones
Tecnologías digitales aplicadas al patrimonio universitario Artículo de revista Revista PH Instituto Andaluz del Patrimonio Histórico, 113 (1), pp. 170-185, 2024, ISSN: 2340-7565. University heritage and technologies : Current Experiences in Andalucia Artículo de revista MUSEA. Journal for museology, museum practice and audience, 1 (1), pp. 160-169, 2024. Deep learning of curvature features for shape completion Artículo de revista Computers & Graphics, 115 , pp. 204-215, 2023. Ordering Artificial Intelligence Based Recommendations to Tackle the SDGs with a Decision-Making Model Based on Surveys Artículo de revista Sustainability, 13 (11), 2021, ISBN: 2071-1050. Inteligencia Artificial y Tecnologías Digitales para los ODS Libro Real Academia de Ingeniería, 2021. V Workshop Internacional de Investigación en Emprendimiento GEM-ACEDE, 2020, ISBN: 978-84-09-23683-1. Nuevas tecnologías para la documentación y difusión del patrionio cofrade Capítulo de libro Valverde, Crespo
J.M. F J (Ed.): La Semana Santa de Granada: Pasado, presente y futuro, pp. 151-191, Ed. Nuevo Inicio, Granada, 2020. Atalaya3D: Disseminating Andalusian Public Universities’ Heritage through 3D and Web Technologies Artículo de revista University Museums and Collections Journal (UMACJ), 11 (1), pp. 43, 2019, ISSN: 2071-7229. Fast collision detection between high resolution polygonal models Artículo de revista Computers & Graphics, 83 , pp. 97-106, 2019, ISSN: 0097-8493. Atalaya3D: Making Universities' Cultural Heritage Accessible Through 3D Technologies Artículo en actas Sablatnig, Robert; Wimmer, Michael (Ed.): Eurographics Workshop on Graphics and Cultural Heritage, pp. 31-35, The Eurographics Association, 2018, ISSN: 2312-6124. CEIG 2017. Proceedings of the XXVII Spanish Computer Graphics Conference Acta de congreso Eurographics Sección Española, EGSE The Eurographics Association, Sevilla, 2017, ISBN: 978-3-03868-046-8. 3DCurator: una herramienta para la inspección de esculturas a través de tomografía computacional Artículo de revista PH: Boletín del Instituto Andaluz del Patrimonio Histórico, (91), 2017, ISSN: 2340-7565. A Complete 3D Information System for Cultural Heritage Documentation Artículo de revista Journal of Cultural Heritage, 23 , pp. 49–57, 2017, ISSN: 1296-2074. Atalaya3D: el portal virtual de patrimonio de las universidades andaluzas Artículo de revista PH: Boletín del Instituto Andaluz del Patrimonio Histórico, (90), pp. 15–16, 2016, ISSN: 2340-7565. A Web 3D-Scene Editor of Virtual Reality Exhibitions and 360-degree Videos Artículo en actas Garcia-Alonso, A; Masiá, B (Ed.): Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (CEIG 2016), pp. 9–13, The Eurographics Association, 2016, ISBN: 978-3-03868-023-9. 3DCurator: A 3D Viewer for CTs of Polychromed Wood Sculptures Artículo en actas Garcia-Alonso, A; Masiá, B (Ed.): Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (CEIG 2016), The Eurographics Association, 2016, ISBN: 978-3-03868-023-9. Out-of-core real-time haptic interaction on very large models Artículo de revista Computer-Aided Design, 77 , pp. 98–106, 2016, ISSN: 0010-4485. Digitalización 3D del Templo de Millones de Años de Tutmosis III Capítulo de libro Seco, M; Jódar, A (Ed.): pp. 349–365, Editorial de la Universidad de Granada, Granada, 2015, ISBN: 9788433857408. EBP-Octree: An Optimized Bounding Volume Hierarchy for Massive Polygonal Models Artículo en actas Juan, M C; Borro, D (Ed.): CEIG - Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (2013), pp. 11–20, The Eurographics Association, 2013, ISBN: 978-84-695-8333-3 . Graphics Systems in a Software Engineering Curriculum Artículo en actas Juan, M C; Borro, D (Ed.): CEIG - Spanish Computer Graphics Conference (2013), pp. 173–176, The Eurographics Association, 2013, ISBN: 978-84-695-8333-3. Proceedings of the 38th Annual Conference on Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, Granada, Spain, April 2010, Acta de congreso Archaeopress, (2494), 2013, ISBN: 978-1-4073-1108-1. Digitalización 3D y Difusión en Web del Patrimonio de las Universidades Andaluzas mediante X3D Y WebGL Artículo de revista Virtual Archaeology Review, 3 (7), pp. 55–59, 2012, ISSN: 1989-9947. Aplicaciones informáticas en Arqueología (Monográfico) Libro Editorial de la Universidad de Granada, 2011, ISBN: 2174-8063. Detección de colisiones en grandes modelos geométricos Artículo en actas Actas del XX Congreso Español de Informática Gráfica, CEIG 2010, Ibergarceta Publicaciones SL, Valencia, 2010, ISBN: 978-84-92812-50-9. Digitalización y reconstrucción de elementos cerámicos arqueológicos de torno Artículo de revista Virtual Archaeology Review, 1 (2), pp. 137–142, 2010, ISSN: 1989-9947. Aplicaciones de la digitalización 3D del patrimonio Artículo de revista Virtual Archaeology Review, 1 (1), pp. 51-54, 2010, ISSN: 1989-9947. Fusion of Cultures. Abstracts of the CAA2010 Libro 2010, ISBN: 978-84-693-0772-4. Real-Time Haptic Rendering on Large Models Artículo en actas Proceedings of the IV Iberoamerican Symposium in Computer Graphics (SIACG'2009), pp. 137–144, Sociedad Venezolana de Computación Gráfica, 2009, ISBN: 978-980-12-3682-5. BP-Octree: Una estructura jerárquica de volúmenes envolventes Tesis doctoral Univ. Granada, 2008, ISBN: 9788469183564. Bounding-Planes Octree: A New Volume-based LOD Scheme Artículo de revista Computer and Graphics, 32 (4), pp. 385–392, 2008. Representación multiresolución de sólidos mediante una jerarquía de planos envolventes Capítulo de libro Joan, R; Torres, J C; Feito, F (Ed.): Herramientas Avanzadas en CAD, Capítulo X, Univ. Jaén, 2007, ISBN: 978-84-690-6855-7. Magic Potter Artículo en actas Hernández, L; Flores, J (Ed.): I Simposium de Informática Gráfica y Patrimonio Histórico (SIGPHI), A Coruña, 2007. Transmisión progresiva de grandes modelos usando una jerarquía de planos envolventes Artículo en actas Cerezo, E; Feito, F (Ed.): XIV Congreso Español de Informática Gráfica (CEIG), Thomson-Paraninfo, Zaragoza, 2007, ISBN: 978-84-9732-595-0. Generación automatizada de modelado 3D para difusión y documentación del patrimonio histórico Artículo en actas Hernández, L; Flores, J (Ed.): I Simposium de Informática Gráfica y Patrimonio Histórico (SIGPHI), A Coruña, 2007. Combining SP-Octrees and impostors for multiresolution visualization Artículo de revista Computer and Graphics, 29 (2), pp. 225–233, 2005, ISSN: 0097-8493. SP-Octrees visualization using impostors Artículo en actas Alexa, M; Galin, E (Ed.): EUROGRAPHICS 2004 Short Presentations, pp. 81–84, The Eurographics Association 2004, ISSN: 1017-4656. Visualización interactiva de SP-Octrees utilizando impostores Artículo en actas Congreso Español de Informática Gráfica (CEIG), pp. 119–123, Edicion Digital @Tres, Sevilla, 2004, ISBN: 84-688-6998-8. A new system for interactive vessel reconstruction and drawing Artículo en actas Enter the past. The E-way into the four dimension of cultural heritage. CAA 2003,Computer Applications and Quantitative Methods in Archaeology, pp. 78–81, Archaeopress, 2004, ISBN: 1 84171 592 1. Virtual Vessel Reconstruction from a Fragment s Profile Artículo en actas Arnold, D; Chalmers, A; Niccolucci, F (Ed.): The 4th International Symposium on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Intelligent Cultural Heritage, pp. 79–88, The Eurographics Association, 2003, ISSN: 1811-864X. On the Interactive 3D Reconstruction of Iberian Vessels Artículo en actas Arnold, D; Chalmers, A; Niccolucci, F (Ed.): The 4th International Symposium on Virtual Reality, Archaeology and Intelligent Cultural Heritage, pp. 71–78, The Eurographics Association, 2003, ISSN: 1811-864X.
2024


2023

2021


2020


2019


2018

2017



2016




2015

2013



2012

2011

2010




2009

2008


2007




2005

2004



2003


